Let's be real. Most articles on data security are boring enough to be prescribed as sleep aids. They list the same tired, generic advice you've heard a thousand times. 'Use strong passwords.' Groundbreaking stuff, right? We've been in the trenches, building a platform that connects companies with elite global talent. Securing a distributed workforce isn't about building a fortress; it's about creating a security culture that travels. It's a whole different beast.
This isn't just another list. Forget the corporate jargon. We’re going to walk through the nine data security best practices that have saved our bacon more than once. These aren't theoretical concepts; they're the battle-tested, pragmatic steps you can implement without mortgaging your office ping-pong table for a team of consultants.
From a Zero Trust model that assumes the bad guys are already inside, to an incident response plan that actually works when things go sideways, we’ll cover what matters. While you can get started with something like an essential network security checklist, think of this guide as the field manual we wish we had when we started. Ready to get real about security?
Forget the old castle-and-moat security model. In a world of remote work and cloud apps, your network perimeter is about as real as a unicorn. Zero Trust is the bouncer at the club door who checks everyone's ID every single time they try to enter a new room. No exceptions. It operates on a simple, slightly paranoid, and highly effective principle: never trust, always verify.
This approach assumes threats are already inside your network, probably sipping a latte and using your guest Wi-Fi. It requires strict identity verification for every person and device trying to access resources, regardless of where they are. Access isn't a one-time thing; it's continuously validated. To really get it, read up on What Is Zero Trust Security And Why It Matters.
Adopting this isn’t a single product purchase; it’s a strategic shift. Here's where to start:
This infographic visualizes the three interconnected pillars that form the foundation of any strong Zero Trust framework.
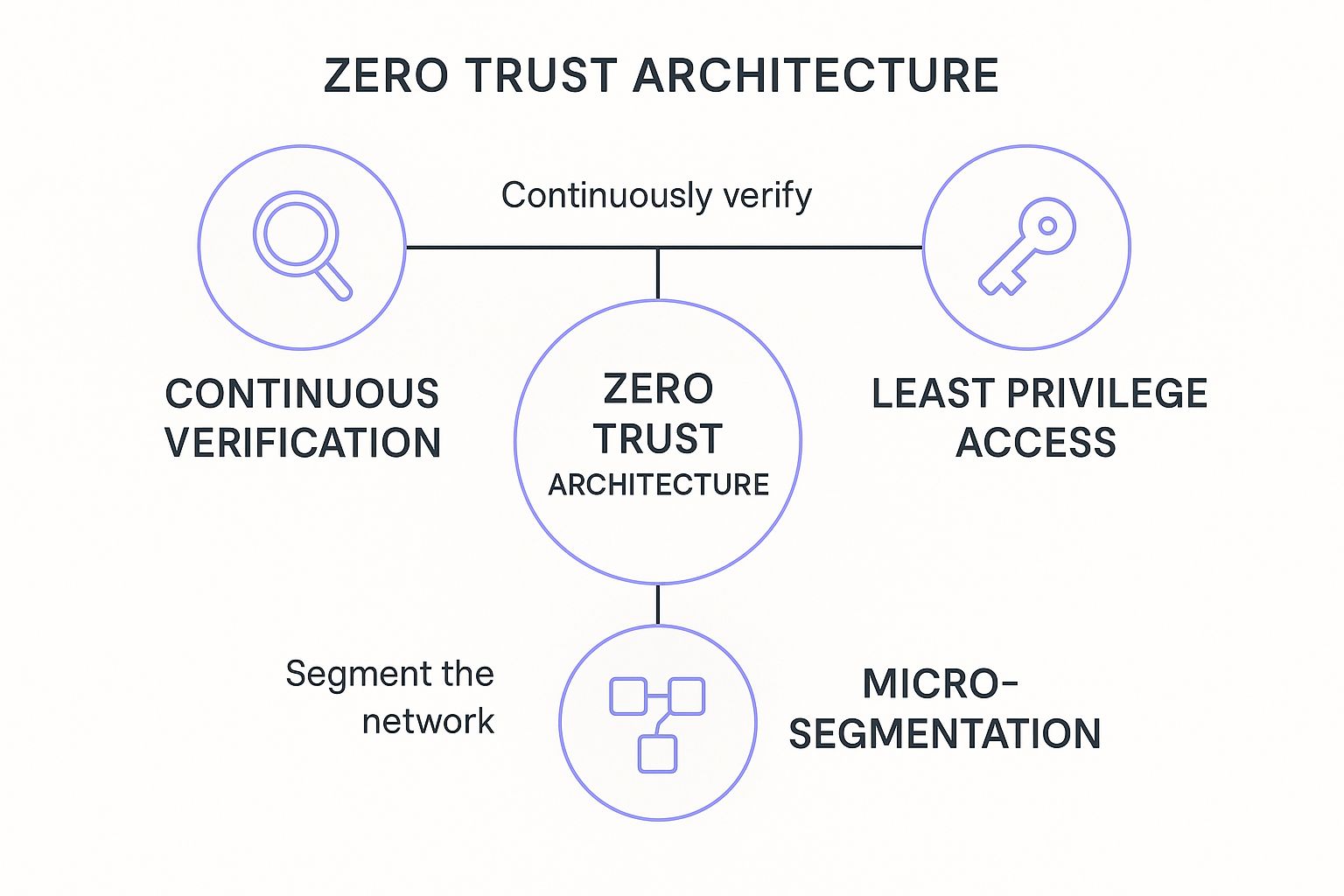
The visualization shows that continuous verification, least privilege access, and micro-segmentation are not standalone concepts but a self-reinforcing security loop. For a distributed team, this is one of the most effective data security best practices because it secures access where it matters: with the user and the app, not some imaginary line around your office.
If passwords are the only thing protecting your company’s crown jewels, you might as well leave the front door wide open with a "please rob us" sign. A single leaked password from some random third-party breach is all it takes. MFA is your digital deadbolt. It's the second or third layer that stops intruders cold, even if they have your password. The concept is bulletproof: prove you are who you say you are with more than just a secret word.
This security practice demands users provide at least two different verification factors to get in. Usually, it's a combo of something you know (password), something you have (your phone), and something you are (your fingerprint). Think of it this way: even if someone steals your house key, they still can't get past the security guard who recognizes your face. It's a fundamental step that shuts down the most common attacks.
Rolling out MFA isn't just about flipping a switch; it’s about making it seamless enough that your team actually uses it. Here’s the no-nonsense way:
For a distributed team, MFA is the highest-impact, lowest-cost security measure you can take. Period.
Leaving your data unencrypted is like leaving your company’s financial records on a park bench. It’s just waiting for the wrong person to come along. Data encryption scrambles your data into unreadable code that can only be deciphered with a specific key. This is a non-negotiable data security best practice that applies to data in two states: at rest (sitting on a server) and in transit (moving across the internet).
If a cybercriminal breaches your defenses and steals a hard drive, encryption is the last line of defense that makes the stolen info completely worthless to them. Think of the end-to-end encryption on Signal; even if someone intercepted your message, they'd just see gibberish. That's what you want for your company's data.

This process is fundamental for securing a modern distributed team, where data is constantly zipping between cloud servers, home offices, and corporate networks. Good encryption means even if a laptop gets stolen from a coffee shop, your data is safe.
Getting encryption right is more than just flipping a switch. It requires a real strategy.
Leaving your security to chance is like driving blindfolded and hoping for the best. You might be fine for a mile or two, but eventually, you're going to hit something. Regular security audits and vulnerability assessments are your GPS and forward-facing cameras, systematically checking your posture before you end up in a ditch. Think of it as a mandatory health check-up for your company's digital soul.
These aren't just for ticking compliance boxes; they are proactive hunts for weaknesses. A vulnerability assessment is like sending a scout to find cracks in your fortress walls. An audit is the full-on inspection by the commanding officer, reviewing your policies and procedures to make sure your defenses actually work. To see what the pros use, check out what industry leaders like Tenable offer.
Running a successful audit isn't about creating a "gotcha" culture; it's about building a stronger company. Here’s how to make it part of your DNA:
If you give every employee a master key to the entire building, don't be surprised when someone eventually leaves the vault door wide open. The Principle of Least Privilege (PoLP) is the common-sense security rule that says you should only give people the keys they absolutely need to do their job, and not a single one more. It's about swapping that master key for a role-specific keycard.
This principle is a core pillar of effective data security best practices because it dramatically shrinks your attack surface. A compromised account can only damage what it can access. If a marketer's account gets hacked, the attackers shouldn't be able to waltz into your source code repository. By restricting access to the bare minimum, you contain the blast radius of any security incident.
This isn't about locking everyone out; it's about giving them exactly what they need. It’s a shift from a "trust by default" to a "need-to-know" mindset.
Let's be honest, your data is one disaster away from disappearing forever. It's not if a hard drive will fail or ransomware will strike, but when. Relying on luck is not a strategy; it's a future catastrophe. Regular data backups and recovery planning are your digital insurance policy, ensuring you can rewind the clock when things inevitably go wrong.
The core idea is simple: have copies of your critical data so you can restore it after an incident. This isn't just dragging files to an external drive once a month. A real strategy is crucial, and a comprehensive guide to backing up data can show you the ropes. Think of Pixar, who nearly lost Toy Story 2 to an accidental rm -rf command, only to be saved by an employee's personal backup. This is one of the most fundamental data security best practices because it's your ultimate undo button.
A backup you can't restore is just a waste of storage. Here's how to make your plan work:
You can have the most expensive firewall on the planet, but it's useless if an employee clicks a malicious link in an email promising free pizza. Your team is your greatest asset, but when it comes to security, they're also your biggest variable. Human error is an eventuality. That’s why turning your team into a human firewall is one of the highest-leverage data security best practices you can implement.
This is about more than a dusty, once-a-year PowerPoint. Effective security training is continuous, engaging, and arms your people with the skills to spot threats. It focuses on recognizing phishing, practicing good password hygiene, and knowing who to call when something smells fishy. The goal is to build a culture where security is everyone's job, not just the IT department's headache.
Ready to move beyond boring compliance videos? Here’s how to create training that actually sticks:
A well-trained team becomes a proactive defense layer, transforming your weakest link into your strongest defense.
If your entire network is one big, open-plan office, a single compromised laptop can quickly turn into a company-wide disaster. Network segmentation is the smart-office equivalent of putting up walls and keycard-access doors between departments. It’s a foundational data security best practice that chops your network into smaller, isolated sub-networks. Firewalls then act as the guards at every door, scrutinizing what's allowed to pass between them.
The strategy is simple: containment. An attacker might breach your marketing network, but they'll hit a digital brick wall when they try to move laterally into your engineering segment. This isn't just a good idea; for many, it's non-negotiable.
Getting started with segmentation doesn't mean you have to rewire your entire office overnight. It's a strategic process.
It’s not if you’ll face a security incident, but when. Believing you're invincible is the fastest way to get blindsided. An Incident Response Plan is your fire drill for a data breach. It’s the pre-written playbook that tells your team exactly what to do when the alarms blare, preventing panic and minimizing the damage. It operates on a critical principle: prepare for the worst, so you can respond at your best.
This moves security from a purely preventative stance to one of readiness. A well-documented plan ensures that when a breach happens, you’re not scrambling to figure out who to call or what to shut down. To see what a real framework looks like, check out the NIST Computer Security Incident Handling Guide.
A plan sitting on a shelf gathering dust is useless. It needs to be a living document. Here's how to build one that works:
A strong incident response plan is what turns a potential catastrophe into a manageable, albeit stressful, event.
| Security Measure | Implementation Complexity | Resource Requirements | Expected Outcomes | Ideal Use Cases | Key Advantages |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Zero Trust Architecture | High – complex initial setup | Significant – org. change, training | Continuous verification, reduced attack surface | Organizations with distributed users, remote work | Enhanced insider threat protection, compliance |
| Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) | Low to Moderate – depends on method | Moderate – tokens, apps, training | Stronger authentication, reduced unauthorized access | Any system requiring secure user access | Cost-effective, compliance support |
| Data Encryption at Rest and in Transit | Moderate to High – technical setup | High – key management, compute | Data confidentiality, integrity maintained | Protection of sensitive data in storage and transit | Meets regulations, defense in depth |
| Regular Security Audits and Vulnerability Assessments | Moderate to High – requires expertise | High – specialized staff, tools | Proactive threat ID, compliance verification | Organizations needing risk management and compliance | Identifies vulnerabilities early |
| Principle of Least Privilege Access | Moderate – ongoing management | Moderate – access controls, audits | Minimized breach impact, reduced insider risk | Enterprises managing large user permissions | Prevents privilege creep, compliance improvement |
| Regular Data Backups and Recovery Planning | Moderate – setup and maintenance | Moderate to High – storage, monitoring | Data loss protection, business continuity | All organizations requiring data availability | Ransomware protection, peace of mind |
| Employee Security Training and Awareness | Low to Moderate – continuous | Moderate – training platforms, time | Reduced human error, security-aware culture | Organizations wanting to reduce social engineering | Cost-effective, improves incident reporting |
| Network Segmentation and Firewalls | High – complex network design | High – hardware/software, expertise | Segmented network, limited breach spread | Environments needing strict network controls | Limits lateral movement, performance benefits |
| Incident Response Planning | Moderate – requires coordination | Moderate to High – planning, drills | Fast containment, reduced business impact | Organizations needing structured incident handling | Improved team coordination, resilience |
We’ve just torn through nine dense, non-negotiable data security best practices. It’s a lot. It’s easy to look at this list, feel a wave of existential dread, and then promptly file it away under “Things I’ll Get To When I Have a Spare Century.”
Don’t do that.
Let’s be brutally honest: implementing robust data security is not a project. It's a continuous, often frustrating, but absolutely critical discipline. It’s like exercise. You don't just "get fit" and then stop. You build a habit, you stay consistent, and you adapt. The goal isn’t to reach a mythical state of "perfect security" overnight. The goal is to build momentum.
Too many founders get trapped thinking they need a massive, budget-breaking initiative to fix everything at once. They admire the problem, map it out in a dozen Gantt charts, hold endless meetings, and then… nothing happens. The sheer scale of the task paralyzes them.
That approach is a recipe for failure. The real secret to mastering data security best practices is to treat it like building any other part of your business: one brick at a time. Don't try to boil the ocean. Pick one thing from our list and knock it out of the park this week.
Here’s your action plan. Choose your own adventure:
As you build out your distributed team, remember that talent and security are two sides of the same coin. You can’t hire world-class remote talent without providing a secure environment for them to do their best work. And you can't build a secure environment without a team that understands why it matters.
This is where the operational backend becomes so critical, especially when you’re sourcing talent internationally. You're not just hiring a developer; you're integrating a new endpoint into your network and a new guardian of your company’s data. This involves navigating complex compliance, payroll, and HR frameworks that are, frankly, a massive headache.
That's a big part of what we do at LatHire. (Toot, toot!) We connect you with pre-vetted, top-tier professionals from Latin America while handling the complex operational infrastructure that keeps everyone secure and compliant. We worry about the international HR and payroll so you can focus on building your product.
The journey to a strong security posture is a marathon, not a sprint. These principles are your roadmap. They are the bedrock of a resilient, trustworthy business. Now, stop admiring the problem. Pick your first step and get moving.
