Let's be honest. For every feature you ship, another three bugs crawl out of the woodwork. You're playing whack-a-mole with your codebase, your customers are getting cranky, and your dev team is one 'critical' ticket away from staging a coup. Sound familiar? I've been there. I've considered mortgaging the office ping-pong table to hire more QA, only to realize we were just catching the same old bugs faster. The problem wasn't a lack of people; it was a lack of a plan.
Turns out, "just test it" isn't a strategy. Shocker, I know. It leads to missed deadlines, bloated budgets, and a product that feels perpetually unfinished. To ship reliable software without burning out your team, you need a disciplined approach. You need to know which tool to pull from the toolbox and when. This isn't just another textbook list of quality assurance testing methods. This is the field guide I wish I had when my startup was held together by caffeine and duct tape.
We're going to break down the 10 essential testing methods that actually move the needle, from the surgical precision of Unit Testing to the real-world gauntlet of User Acceptance Testing (UAT). We’ll cut through the academic jargon and give you the real-world take on what works, what doesn't, and where to deploy each technique for maximum impact. This guide will help you understand not just the what, but the why and how behind a robust testing strategy. Ready to turn that war zone into a well-oiled machine? Let's dive in.
The Microscopic Inspection.
Unit testing is the bedrock of sane software development and one of the most fundamental quality assurance testing methods you can adopt. Think of it as inspecting every single brick before you build the wall. Instead of testing the entire application at once, developers write small, automated tests for individual components or "units" of code—a single function, a method, a class. The goal? To prove that each tiny piece of the codebase works exactly as intended in complete isolation.
This granular approach means that if a bug appears later, you know it’s not because the core building blocks are faulty. It’s a massive shortcut for debugging, pinpointing issues at their source long before they get tangled up with other components. For example, Amazon doesn't just hope its payment processing modules work; they have armies of unit tests ensuring a single function, like calculateSalesTax(), behaves predictably every single time.

Ignoring unit testing is like trying to find a single typo in a 1,000-page book after it's been printed. It's expensive, soul-crushing, and frankly, stupid. This method is your first line of defense, catching errors early when they are cheapest and easiest to fix. It also doubles as living documentation for your code; a well-written test tells another developer precisely what a piece of code is supposed to do.
To implement unit testing effectively, don't just chase 100% code coverage. That's a vanity metric that leads to terrible, useless tests. Focus on quality and clarity.
test_CalculateTotal_WithNegativeQuantity_ThrowsException. This makes test reports instantly understandable without even looking at the code. No more test1, test2, finalTest.Making Sure the Bricks Play Nice.
If unit testing is checking each brick, integration testing is making sure those bricks form a sturdy, connected wall. This crucial member of the quality assurance testing methods family focuses on verifying how different software modules or services talk to each other. The goal is to expose defects in the interfaces and the data flow between integrated components. You're no longer asking "does this one thing work?" but "do these things work together?"
This is where you catch the problems that only show up when separate parts of your system start interacting. Think PayPal. It lives and breathes integration testing to ensure its payment gateway seamlessly connects with thousands of different e-commerce platforms. A single failed handshake between systems could mean millions in lost revenue, so they test every possible interaction relentlessly.
Skipping this step is like assembling IKEA furniture without instructions. Sure, each part might be perfectly made, but you’ll end up with a wobbly chair that collapses the moment someone sits on it. Integration testing is your reality check, revealing the faulty assumptions developers made about how their code would interact with someone else's. It finds data format mismatches, API call failures, and authentication issues before your users do.
Effective integration testing requires a plan, not just throwing components together and hoping for the best.
The "Did I Break Something?" Insurance Policy.
Regression testing is the "don't break what's already working" sanity check of software development. It's one of the most critical quality assurance testing methods for maintaining stability as you grow. Think of it as a paranoid re-check after every change you make. You’ve just added a shiny new feature or fixed a bug, but did you accidentally shatter something else in the process? Regression testing answers that question by re-running a suite of existing tests to ensure that old, reliable functionality remains intact.
This is how you avoid the dreaded "one step forward, two steps back" dance that haunts development teams. When Facebook tweaks its News Feed algorithm, they don't just test the new logic. They run a massive battery of automated regression tests to confirm that core features like posting, liking, and messaging haven't suddenly imploded. It's the safety net that allows for rapid, continuous deployment without constant fear.
Skipping regression testing is like a surgeon performing a delicate operation and then leaving without checking if the patient's heart is still beating. It introduces massive, unpredictable risk. A minor change in a payment module could inadvertently break the user login process. This method ensures that enhancements don't create more problems than they solve, safeguarding user trust and preventing costly, embarrassing rollbacks.
Effective regression testing is about being smart and strategic, not just re-running every test ever written. Your goal is to maximize confidence while minimizing execution time.
Does This Thing Actually Do the Thing?
If unit testing is checking the bricks, functional testing is making sure the wall actually stands up and does its job. This is a type of quality assurance testing method that completely ignores how the code works internally (a "black-box" approach) and focuses solely on what it does. Does the login button actually log you in? Does the "Add to Cart" feature add the correct item? You’re testing the software against its specified functional requirements, just like a user would.
The goal is to simulate real user scenarios to confirm that the application behaves as expected from the user's perspective. Think about Airbnb: functional tests would verify that a user can search for a location, filter by dates, select a property, and successfully complete a booking. It’s not about checking a single function; it's about validating a complete business process from start to finish.
Skipping functional testing is like building a car with a powerful engine but forgetting to connect the steering wheel to the tires. It might look great on paper, but it’s utterly useless to the end-user. This method ensures that the product you’re shipping actually solves the problem it was designed for. It bridges the gap between technical implementation and business requirements, answering the most important question: "Does this thing actually work?"
Effective functional testing is about discipline and a user-centric mindset. It’s not just about clicking buttons randomly.
test@test.com and a password of 1234 is a start, but it’s lazy. Use data that mirrors what a real user would input, including special characters, different languages, and weird formats.The Trial by Fire.
Performance testing is less of a test and more of a public shaming for your application. This is where you find out if it can handle the spotlight or if it will buckle under pressure. As one of the most critical quality assurance testing methods, it simulates real-world user traffic to measure an application's speed, stability, and scalability. The goal isn't to see how your system behaves with one user, but with thousands, or even millions, hammering it at the same time.
Will your e-commerce site survive the Black Friday rush, or will it crash and burn, taking your revenue with it? Walmart obsessively load tests its platform for this exact scenario. Ticketmaster uses performance testing to guarantee its systems don't collapse the second tickets for a superstar's tour go on sale. It's about finding and fixing bottlenecks before your users find them for you.
Skipping performance testing is like launching a rocket without checking the fuel lines. It might look good on the launchpad, but it’s destined for disaster. A slow, unresponsive application doesn't just frustrate users; it actively drives them away and demolishes your brand's reputation. This method ensures your application provides a smooth, reliable experience, even at peak demand, protecting both your users and your bottom line.
Effective performance testing is about creating realistic chaos in a controlled environment.
Hiring a Bouncer for Your Code.
Security testing isn't just a "nice-to-have" checkbox; it's a critical quality assurance testing method that protects your software from the digital boogeymen. Think of it as hiring a professional security detail for your application. It’s an investigative process designed to find and fix vulnerabilities, threats, and risks before malicious actors find and exploit them. This isn't just about preventing hackers; it's about protecting your data, your users, and your company's reputation.
This type of testing involves a barrage of simulated attacks, vulnerability scans, and code reviews to ensure your system's defenses hold up under pressure. It’s how financial giants like JPMorgan make sure their mobile banking apps are fortresses. Ignoring this is like leaving your front door wide open with a sign that says, "Free data inside."

A data breach isn't just an IT problem; it's a business-ending catastrophe that can evaporate customer trust overnight. Security testing is your proactive defense, moving from a reactive "clean up the mess" posture to a preventative "stop the mess from happening" strategy. It ensures you're not just compliant with regulations like HIPAA or GDPR but are genuinely protecting sensitive information. For a deeper dive, review these data security best practices from lathire.com.
Effective security testing is a mindset, not a single event. It requires continuous vigilance and a healthy dose of paranoia.
The Final Boss: The Actual User.
After all the code has been written, integrated, and blitzed by internal QA, there's one final, terrifying question: "But will anyone actually use it?" User Acceptance Testing (UAT) is the final checkpoint where real users validate the software against their business requirements in a production-like environment. This isn't about finding technical bugs; it's about confirming the software solves the real-world problem it was built for.
Think of it as the dress rehearsal before opening night. This is where you hand the keys to the end-users and ask if the car drives the way they expect. It’s one of the most critical quality assurance testing methods because it directly answers whether the project was a success from a business perspective.
Skipping UAT is like designing a five-star menu without ever letting a chef taste it. You might have technically perfect code, but if it creates more work for the user or doesn't match their workflow, your beautiful software will gather digital dust. UAT is your last chance to find fatal usability flaws, incorrect business logic, or process gaps before they impact your actual customers and your bottom line. It’s the ultimate reality check.
Effective UAT is less about testing and more about validation. It requires a completely different mindset.
Teaching a Robot to Do the Boring Stuff.
Automated testing is where you teach a robot to do the repetitive, mind-numbing work so your human testers can focus on what they do best: thinking critically and trying to break things in creative ways. It uses specialized software tools to execute test cases, compare actual outcomes with expected results, and report on the findings, all without manual intervention. Think of it as creating a tireless digital twin of your QA team that can run thousands of checks overnight.
This approach is the engine behind modern continuous integration and continuous delivery (CI/CD) pipelines. Companies like Tesla rely on it to validate critical software updates for their vehicles before they ever hit the road. It’s not just about speed; it’s about creating a repeatable, reliable, and scalable safety net for your entire development process.
Trying to scale a modern software product without automation is like trying to empty the ocean with a bucket. You’ll burn out your team and miss critical bugs. Automated testing is your best defense against regression errors—the nasty bugs that reappear in previously working code after a new feature is added. It provides rapid feedback, allowing developers to know if their latest commit broke something within minutes, not days.
Jumping into automation without a strategy is a recipe for a flaky, unmaintainable test suite that everyone ignores. To get it right, you need discipline and a clear plan. If you are hiring for these roles, it is also important to consider using pre-employment skills testing platforms to find the right candidates.
Going Off-Script.
If scripted testing is like following a detailed recipe, exploratory testing is like being a chef on Chopped. You get a basket of ingredients (the application) and are told to create something amazing on the fly. This is one of the most human-centric quality assurance testing methods, relying on the tester's creativity, intuition, and experience rather than a predefined script. Testers simultaneously learn the system, design tests, and execute them, hunting for bugs that rigid test cases would never find.
This unscripted approach is a powerful way to uncover complex, unexpected issues. Think of it as controlled chaos. Video game companies live and breathe this method to find bizarre gameplay glitches. It’s less about confirming what should work and more about discovering what could break.
Relying solely on scripted tests is like only looking for your lost keys under the lamppost because that's where the light is. You miss everything else. Exploratory testing shines a flashlight into the dark corners of your application, finding usability flaws, weird edge cases, and show-stopping bugs that no one thought to write a script for. It’s your best defense against the "unknown unknowns."
To prevent exploratory testing from becoming just random clicking, you need to add a bit of structure to the freedom. It's about focused investigation, not aimless wandering.
Making Quality Everyone's Problem.
Continuous testing isn't a type of test; it's a philosophy. It transforms quality assurance from a final gate into an ongoing, automated process baked into the software delivery pipeline. Instead of testing in a separate, isolated phase, this method integrates automated tests directly into every stage. The goal is to get immediate feedback on the business risks associated with every single code change, from commit to production. It’s about building quality in, not inspecting for it later.
This approach is what allows giants like Amazon to deploy new code every few seconds without setting the internet on fire. By executing a suite of automated tests at every stage, they can validate quality continuously. This shift-left (testing early) and shift-right (monitoring in production) mindset ensures that potential issues are caught instantly, making releases faster, safer, and remarkably less stressful.
The following infographic illustrates the core relationships between the essential components of a successful continuous testing strategy.
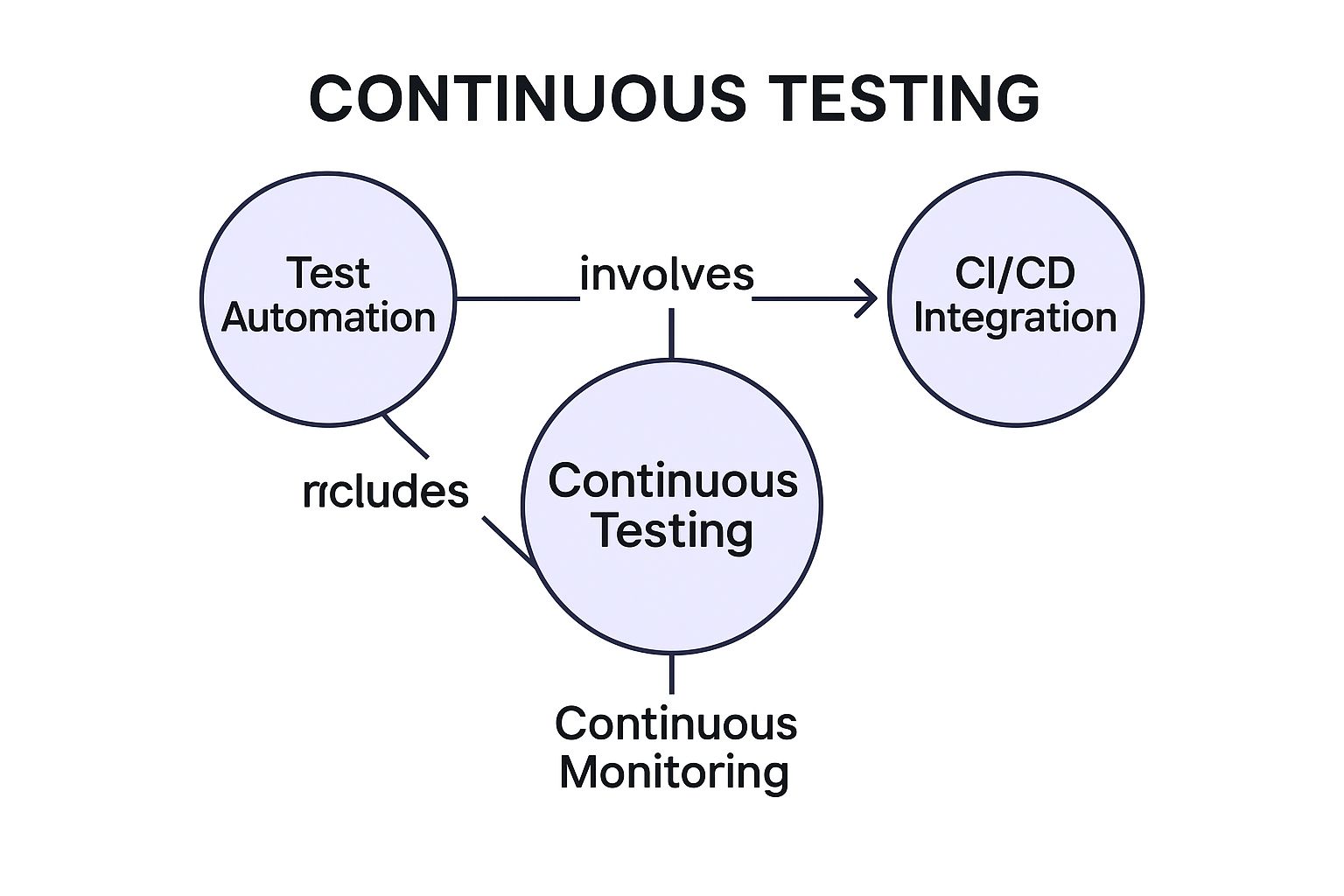
As the concept map highlights, test automation is the engine that drives feedback within the CI/CD pipeline, while continuous monitoring provides the real-world validation needed to close the loop.
Trying to achieve a fast, reliable release cadence without continuous testing is like trying to drive a Formula 1 car with your eyes closed. You might move forward for a bit, but a catastrophic failure is inevitable. This method is the ultimate risk-mitigation strategy, providing a constant stream of feedback that allows teams to build, test, and release with confidence. It dismantles the traditional "quality bottleneck" and makes quality a shared responsibility across the entire team.
To truly benefit from continuous testing, you need more than just a few automated scripts. It requires a cultural and technological shift.
| Testing Type | Implementation Complexity | Resource Requirements | Expected Outcomes | Ideal Use Cases | Key Advantages |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Unit Testing | Low to moderate; requires developer effort | Minimal; developer time and test frameworks | Early bug detection, improved code quality | Testing individual code units | Fast feedback, supports refactoring, high coverage |
| Integration Testing | Moderate to high; involves multiple components | Moderate; test environment and integration tools | Detect interface and data flow issues | Validating module interactions | Catches integration defects missed by unit tests |
| Regression Testing | Moderate; requires maintaining existing test suites | High initially; automation tools and maintenance | Ensures unchanged functionality after changes | Verifying impact of code modifications | Prevents regressions, supports continuous delivery |
| Functional Testing | Low to moderate; based on requirements | Moderate; testers and test management tools | Verifies software meets business specs | Validating user-facing functions | User-focused, ensures requirement fulfillment |
| Performance Testing | High; specialized tools and expertise needed | High; test environments, tools, and infrastructure | Measures system behavior under load | Load, stress, and scalability testing | Identifies bottlenecks, improves user experience |
| Security Testing | High; needs security expertise and tools | High; security specialists and testing tools | Identifies vulnerabilities and protects data | Ensuring application security | Prevents data breaches, ensures compliance |
| User Acceptance Testing (UAT) | Low to moderate; conducted by end-users | Low to moderate; user involvement and environment | Validates business requirements with users | Final validation before release | Confirms usability and business alignment |
| Automated Testing | Moderate to high; scripting and tool setup | Moderate to high; automation frameworks and skills | Faster test execution, frequent feedback | Repetitive and regression test cases | Increases coverage, reduces manual effort |
| Exploratory Testing | Low; flexible and unscripted | Low; skilled testers and minimal setup | Finds unexpected bugs and usability issues | Early testing, unclear requirements | Rapid feedback, creative defect discovery |
| Continuous Testing | High; integrates across lifecycle and tools | High; automation, CI/CD tools, skilled teams | Immediate quality feedback throughout delivery | DevOps, Agile continuous delivery processes | Accelerates delivery, reduces risks, optimizes testing |
So there you have it. Ten different ways to poke, prod, and pressure-test your product until it's ready for the wild. We’ve walked through everything from the microscopic precision of Unit Testing to the big-picture validation of User Acceptance Testing. We’ve seen how Regression Testing acts as your safety net and how Performance Testing ensures you don’t buckle under your own success.
If you walk away with one thing, let it be this: there is no single magic bullet. Quality isn't a department you delegate to or a final step you rush through before a launch. It’s a culture. It’s a strategic, layered approach that combines multiple quality assurance testing methods to build a fortress around your user experience. You can’t just unit test your way to a five-star rating, and you certainly can’t throw a few exploratory testers at a buggy build and hope they find the critical flaws.
The real goal isn’t just finding bugs. It’s about building a system so robust, so resilient, that bugs have a harder time surviving in the first place.
The teams that ship with swagger aren't the ones using just one of these methods. They’re the ones who have mastered the blend. They’ve woven a tapestry of quality checks throughout their entire development lifecycle.
Picking the right combination of these quality assurance testing methods is what separates the teams that deploy and relax from the ones who deploy and pray. It's the difference between a minor hotfix and a full-blown, weekend-ruining rollback.
Building this quality-driven culture is one thing. Staffing it is a whole other beast. Finding a developer who’s a unit testing evangelist, an automation engineer who can build a framework from scratch, and a security expert who thinks like a hacker is a monumental task.
Hope you enjoy spending your afternoons fact-checking resumes and running technical interviews—because that’s now your full-time job. You get to sift through candidates who say they understand continuous testing but have never actually implemented a CI/CD pipeline. Good times.
Or… you could let someone else do the heavy lifting.
At LatHire, we’ve built a pipeline of pre-vetted, top-tier tech talent from Latin America who live and breathe this stuff. (Toot, toot!) We’re not just a database of resumes; we’re a curated network of professionals who have already proven their expertise.
We connect you with pros who can build your automation frameworks, secure your applications, and hunt down bugs with ruthless efficiency. This means you can get back to what you do best: building your business, not building a hiring function. The objective isn't just to test your product; it's to build a process and a team that ensures quality from day one. Now go build yours.
